Gall Bladder Stone (Cholelithiasis)
The cost of laparoscopic gallbladder surgery in India can vary depending on factors such as the specific hospital or clinic, the surgeon's experience and reputation, the patient's medical history and condition, and other factors. However, compared to other countries, the cost of medical treatment in India is generally lower, making it an attractive option for patients who are looking for affordable medical care.
In addition to the lower cost of medical treatment, patients who choose to undergo laparoscopic gallbladder surgery in India can benefit from the expertise of highly skilled surgeons and access to state-of-the-art medical facilities. Many hospitals and clinics in India offer advanced laparoscopic techniques and equipment, as well as a range of other medical services and amenities.
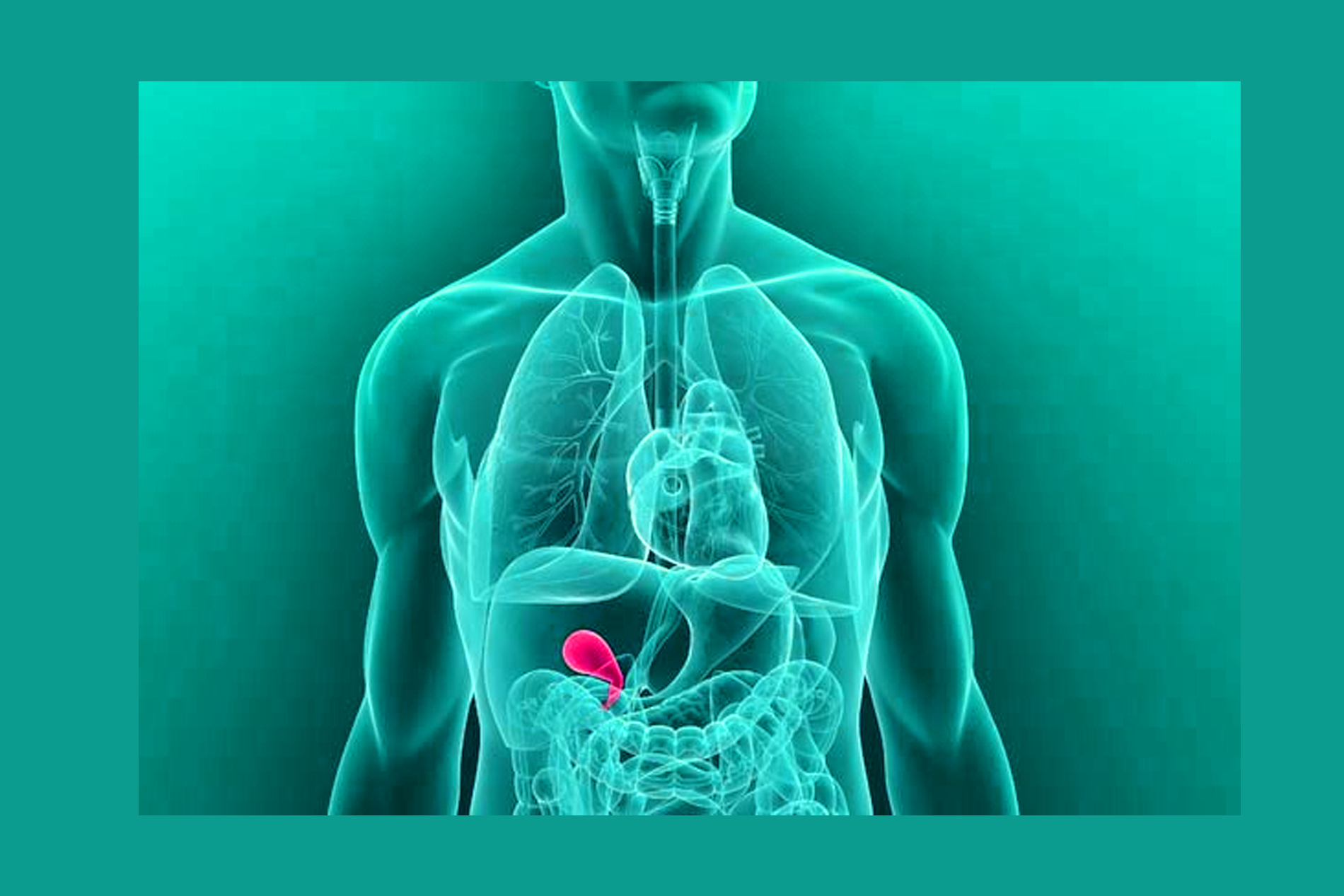
The gallbladder is a small pear-shaped organ located on the right side of the abdomen, just beneath the liver. Its main function is to store and release bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver that helps to break down fats in the small intestine.
When food enters the small intestine, the gallbladder releases bile through a small duct called the cystic duct. The bile mixes with the food and helps to break down fats, making them easier for the body to absorb.
The gallbladder is not considered a vital organ, and it is possible to live without it. However, if the gallbladder is not functioning properly, it can lead to a range of digestive problems and discomfort. In some cases, surgical removal of the gallbladder, known as a cholecystectomy, may be necessary to relieve these symptoms. This procedure can be performed using open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery, depending on the patient's individual case and needs.
What Causes Gallbladder Problems?
There are several factors that can contribute to gallbladder problems, including:
1. Gallstones: These are the most common cause of gallbladder problems. Gallstones are hard deposits that form in the gallbladder or bile ducts, and can cause blockages that lead to pain, inflammation, and infection.
2. Inflammation: Inflammation of the gallbladder, also known as cholecystitis, can be caused by a blockage of the bile ducts or infection.
3. Bile duct obstruction: A blockage in the bile ducts can cause bile to build up in the gallbladder, leading to inflammation and other problems.
4. Tumors or growths: Rarely, tumors or other growths can form in the gallbladder, causing pain and other symptoms.
5. Other medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as liver disease or pancreatitis, can increase the risk of developing gallbladder problems.
6. Genetics: In some cases, a family history of gallbladder disease can increase the risk of developing gallstones or other gallbladder problems.
Certain lifestyle factors can also contribute to gallbladder problems, such as a high-fat diet, obesity, and rapid weight loss. Women are also more likely than men to develop gallbladder problems, particularly during pregnancy or as they age. If you are experiencing symptoms of gallbladder problems, it is important to talk to your doctor to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
How Are These Problems Found And Treated?
Gallbladder problems are typically diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, medical history, imaging tests, and blood tests. Your doctor may also recommend other tests, such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, to help determine the cause of your symptoms.
Treatment for gallbladder problems depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as dietary modifications or weight loss may be recommended to help manage symptoms. Medications may also be prescribed to dissolve gallstones or manage inflammation.
Surgery is often recommended for more serious gallbladder problems, particularly if you are experiencing persistent pain or complications such as infection. The most common type of surgery for gallbladder problems is a cholecystectomy, which involves removing the gallbladder. This can be done using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery.
Laparoscopic surgery is a less invasive option that typically involves smaller incisions, less pain, and faster recovery times compared to open surgery. Your doctor will help you determine the best course of treatment based on your individual needs and the severity of your condition.
In some cases, alternative treatments such as herbal remedies or acupuncture may be recommended to help manage symptoms, but it is important to discuss any alternative therapies with your doctor before trying them.
What Are The Advantages Of Performing The Procedure Laparoscopically?
Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery, is a surgical technique that involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a camera and specialized instruments to perform the procedure. Here are some advantages of performing the procedure laparoscopically:
1. Less pain and scarring
2. Shorter hospital stays
3. Fast recovery time
4. Reduced risk of infection
5 Better visualization
6 Lower blood loss
What Preparation Is Required For Gall Bladder Surgery In India?
Preparation for gallbladder surgery in India may vary depending on the type of surgery and the individual patient's needs. However, here are some common preparations that may be required before gallbladder surgery:
1. Consultation with the surgeon: Before the surgery, you will need to have a consultation with the surgeon who will perform the surgery. The surgeon will examine your medical history and perform a physical examination to assess your fitness for surgery.
2. Diagnostic tests: The surgeon may order diagnostic tests such as blood tests, ultrasound, or MRI to assess the condition of your gallbladder and to identify any potential complications.
3. Medication review: Your surgeon will review all of your current medications, including any over-the-counter medications and supplements, to determine if any of them need to be stopped or adjusted before the surgery.
4. Fasting: You will be required to fast for a certain period before the surgery. This is to ensure that your stomach is empty and reduce the risk of complications during and after the surgery.
5. Preoperative medications: Your surgeon may prescribe medications to take before the surgery to reduce pain and inflammation and to prevent infection.
6. Anesthesia: The surgeon will discuss the type of anesthesia that will be used during the surgery, either general or regional anesthesia, and any potential risks or complications associated with it.
7. Hospital admission: Depending on the type of surgery, you may need to be admitted to the hospital a day before the surgery for observation and preparation.
8. Follow-up care: After the surgery, you will need to follow the surgeon's instructions for postoperative care, including medication management, wound care, and diet.
It's important to follow all instructions from your surgeon and medical team to ensure a safe and successful gallbladder surgery.
Steps in Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal -
Laparoscopic gallbladder removal, also known as laparoscopic cholecystectomy, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the gallbladder. Here are the general steps of the procedure:
1. Anesthesia: Before the surgery begins, the patient is given general anesthesia to ensure that they are asleep and feel no pain during the procedure.
2. Incisions: The surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdomen, usually around the belly button and upper right quadrant of the abdomen.
3. Insertion of laparoscope: A laparoscope, which is a long, thin tube with a camera on the end, is inserted through one of the incisions. The camera sends images of the inside of the abdomen to a monitor in the operating room, allowing the surgeon to see the gallbladder and surrounding organs.
4. Insertion of surgical instruments: Small surgical instruments are inserted through the other incisions to cut and remove the gallbladder.
5. Dissection of the gallbladder: The surgeon uses the surgical instruments to carefully separate the gallbladder from the liver and bile ducts. Once the gallbladder is completely separated, it is removed through one of the incisions.
6. Closing the incisions: The small incisions are closed with stitches or surgical glue.
7. Recovery: After the surgery, the patient is taken to the recovery room and monitored for several hours. Most patients are able to go home the same day or the following day, depending on their recovery.
Laparoscopic gallbladder removal is generally considered a safe and effective procedure, and it typically results in a faster recovery and less pain compared to traditional open surgery. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are some risks, including bleeding, infection, and damage to nearby organs. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of the surgery with your doctor before deciding to undergo the procedure.
What After Gallbladder Surgery?
After gallbladder surgery, also known as a cholecystectomy, you can expect some changes in your body and daily routine. Here are some things you may experience:
1. Pain and discomfort: You will likely experience some pain and discomfort around the incision site and in your abdomen. Your doctor will prescribe pain medication to help manage the pain.
2. Diet changes: Your doctor may recommend that you follow a low-fat diet for a few weeks after surgery to help your body adjust to the absence of the gallbladder. You may also experience digestive changes and may need to avoid certain foods or eat smaller, more frequent meals.
3. Activity restrictions: You may need to limit physical activity for a few weeks after surgery, and avoid heavy lifting and strenuous exercise.
4. Follow-up appointments: Your doctor will schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery and check for any complications.
5. Short hospital stay: Most people are able to go home the same day or the day after the surgery.
6. Possible complications: While gallbladder surgery is generally safe, there are some possible complications, such as infection, bleeding, or injury
What Complications ?
Complications can occur in various medical conditions and situations. Below are some examples of possible complications that can occur:
1. Surgery: Surgery is a medical procedure that carries the risk of complications. Complications may include excessive bleeding, infection, anesthesia reactions, blood clots, and damage to surrounding organs or tissues.
2. Pregnancy: Pregnancy is a natural process, but it can also lead to various complications. Some of the possible complications include gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, preterm labor, fetal distress, and stillbirth.
3. Chronic diseases: Chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and kidney disease can cause various complications. For example, diabetes can cause nerve damage, kidney damage, vision problems, and circulation problems.
4. Infections: Infections can lead to various complications depending on the type and severity of the infection. For example, bacterial infections can lead to sepsis, while viral infections can lead to complications such as pneumonia or encephalitis.
5. Trauma: Trauma can lead to various complications, including bleeding, shock, infection, organ damage, and long-term disability.
6. Medications: Medications can cause complications in some cases. For example, some medications can cause allergic reactions, side effects, or interactions with other medications.
It's important to note that not all medical conditions or situations will result in complications. However, it's essential to be aware of the possible complications and take measures to prevent them where possible. If you're concerned about potential complications related to your health, speak with a healthcare provider.
When to Call Your Doctor?
It is important to call your doctor if you experience any concerning symptoms or changes in your health. Here are some situations when you should consider calling your doctor:
1. Emergency situations: If you have a medical emergency, such as chest pain, difficulty breathing, or severe bleeding, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room right away.
2. New or worsening symptoms: If you have new or worsening symptoms, such as fever, cough, headache, abdominal pain, or rash, call your doctor to discuss whether you need to be seen in person.
3. Medication side effects: If you are experiencing any side effects from your medications, such as dizziness, nausea, or allergic reactions, contact your doctor as soon as possible.
4. Chronic health conditions: If you have a chronic health condition, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or asthma, and your symptoms are worsening or not improving with your current treatment, contact your doctor.
5. Routine check-ups and screenings: Don't forget to schedule regular check-ups and screenings with your doctor, even if you feel healthy. These appointments can help identify potential health issues before they become serious.
Overall, it's important to trust your instincts and call your doctor if you have any concerns about your health or the health of a loved one.